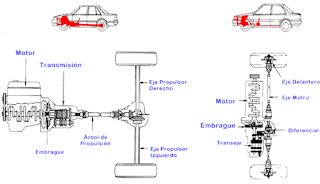
The transmission is the set of mechanisms to transmit torque to the wheels, increasing up the courage to start and ride at all speeds, through a series of des multiplications. It also allows the vehicle from a standing start, keep the engine running while the vehicle stationary, and allow such movement back to park.

What elements compose?
PROPELLER SHAFT
EI drive shaft is a device that connects the transmission to the rear differential FR vehicle (front-engine, rear drive) and 4WD (4 wheel drive). In addition, it is designed to transmit power differential due to the continuous changes in angle and length to it, since this is always moved up and down or back and forth in response to potholes or paths on the surface of the and tracks changes in vehicle loading. The shaft is made of a hollow steel pipe, which is light in weight and strong enough to resist twisting and bending. A universal joint is mounted on each of the shaft ends. Furthermore, it is constructed so that the portion connected to the transmission to respond to changes in length.

UNIVERSAL UNION
The universal joint (crosshead) responds to changes in the angle of connection of the drive shaft so that the power can be easily transmitted. Its construction is simple and reliable operation is being used widely. A universal joint is made by assembling a shaft yokes shaped crosshead interlocked by bearings. The part that connects to the transmission is also slotted (with their teeth to each other are connected to a shaft or a hole), making it possible for the shaft slide forward or backward to dampen the changes in length of connection.
DIFFERENTIAL
Differential function is divided equally torque produced by the engine and pass it to the driving wheels, while allowing these rotate at different speeds if necessary. This occurs when the car enters a bend in the road; that's when the wheels of the axle shafts rotate at different speeds.
The differential reduces the rotational speed transmitted from the gearbox and increases the strength of movement, and also distributes the force of movement in the left and right direction transmitting this movement to the wheels.
CLUTCH
Set pieces for connecting or disconnecting the engine gearbox to make it possible to carry out a gear change and the setting in motion of the car. Pressing the foot pedal clutch is disengaging, ie, separating the clutch members, the box being disconnected engine changes; Crankshaft and input shaft in the gearbox are separated. Releasing the pedal, after another driving speed getting into the box, the two shafts rotate together again and fully engaged.
GEAR BOX
Gear set, usually four and one reverse, that enable to vary the rotation of the motor (and therefore their power) without altering the actual vehicle speed. There are two types of gearboxes: the manual and automatic. In the first is the driver himself who has to choose at all times the traction you need the vehicle for the type of work he has to do, namely, to maintain a certain pace of ongoing or to overcome difficulties that can present the route followed. In the second case, when the box is automatic, it has the precise mechanisms so that, without driver intervention, they will produce the precise changes in the gears so that the walking pace is maintained.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
The automatic transmission is a transmission system that is capable by itself to select all gears or relationships without the need for direct intervention of the driver. The change from one relationship to another occurs as a function of both the vehicle speed and the speed of the engine, so that the driver needs no clutch pedal or gearshift. Simply stepping on the accelerator pedal causes the ratio change as the engine revs varies. The result is the driver who appreciates the convenient change that produces no jerking and allows you to give full attention to the traffic. Therefore the automatic transmission not only provides more comfort, but provides the greatest active safety vehicle.
The key elements that make up most of the current automatic transmissions are:
a hydraulic torque converter that varies and automatically adjusts its output torque, the torque transmission needs.
an epicyclic train or a combination thereof to provide the different gear ratios.
a control mechanism that automatically selects the relations of the planetary gear sets. This control system can be both mechanical and hydraulic, electronic or a combination thereof.
Precisely the electronic control is the biggest innovation available to current automatic changes giving the driver the choice between several driving programs (economic, sports, winter) by Unilever, now reaching control systems exist that can automatically select change the program best suited to each particular driving situation gears.
Among the data that use these systems to their calculations are, the frequency with which the driver steps on the brake, the slope of the road, the number of curves of the same, etc.
TYPES OF TRANSMISSION
Depending on where the motor is positioned and which shaft is rotated by the engine that distendimos the following transmission rates:
FRONT WHEEL DRIVE
Used on medium power vehicles of this type the front wheels are receiving the motor rotation while also those for steering the vehicle.
This type of transmission shaft has since obviously no need
FRONT WHEEL DRIVE
System rarely used due to cooling problems this system has rear-wheel drive like its engine.
TRANSMISSION 4X4
The four-wheel drive, four-wheel drive or all-wheel drive is an expression commonly used to refer to passenger cars and two-axle road. Usually abbreviated as 4 × 4 or 4WD, is a transmission system in a car in which all the wheels can receive power from the engine simultaneously. Most road cars and trucks have four-wheel drive, as well as some sports cars and high-end.
Permanent 4x4 all-wheel drive
This permanent four wheel drive system, also known as AWD always distributes traction to all four wheels. The pulling force of the engine is transmitted to the center differential through the transmission, and from there to all four wheels.
AWD 4x4 connectable
This system is based on permanent drive one, and the other axis is connected to the engine by changing system according to the will of the driver, or automatically by an electronic system that detects road conditions. This type of traction is most commonly used in middle road or economic range.
WHAT ROLE DOES TRANSMISSION?
The transmission function is to get different speeds in
the engine and wheels for better use of engine power and spread between the
wheels, as required by the vehicle.
VIDEOS OF INTEREST
ROLE OF TRANSMISSION
CLUTCH
DIFFERENTIAL
TRANSMISSION
4X4 OR TRANSFER CASE